What is Pseudonymization? Your Practical Guide to the GDPR

Today, with so many data breaches happening, it's very important to keep personal information safe. Pseudonymization is a key way to do this, especially online. In this article we are discussing what pseudonymization is and why it's important for keeping personal data private, in line with the requirements of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
What is Pseudonymization in Data Privacy?
Pseudonymization, a word derived from the Greek word “pseudṓnymon,” refers to what the Cambridge Dictionary calls “a process in which information that relates to a particular person, for example, a name or email address, is changed to a number or name that has no meaning so that it is impossible to see who the information relates to.”
In data privacy then this is a way for you to keep personal data safe by changing it so nobody can tell what it refers to or who it belongs to without having the extra information required to decode it. By using this data management and de-identification process you transform the personal information of data subjects in such a way that the resulting information can only be attributed to a specific data subject with the help of additional information, a key of sorts, which has to be kept separate and secure from the original data to ensure the privacy of data subjects.
In effect, pseudonymization helps your business to mitigate privacy risks, which makes this technique a cornerstone in data privacy.
But how does pseudonymization work, you ask?
Imagine that your name is replaced with a sequence of numbers and letters which form a unique identification code that only your doctor knows. Even if someone else sees your medical records they won’t know it refers to you unless they have the decoding key that matches your name to the numbers and letters in the code.
Pseudonymization hides the identity of the data subject inside the data, making it harder for unwanted eyes to figure out who is who, which is why it is really important for keeping information private and is a big part of data privacy.
However, pseudonymization is more than just a simple disguise of data; it is a strategic approach to personal data protection that significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and personal data misuse, making it a valuable tool in those contexts where data sharing and data analysis are necessary. Returning to the health record example above, in medical research, pseudonymization allows for patients’ data to be used in studies without disclosing any sensitive health information to the researchers. This way, patient confidentiality is maintained while scientific advancements are made.
Pseudonymization isn't a one-size-fits-all solution; it can be changed to fit the level of privacy required and the risks involved, making it a useful tool for keeping personal data safe while still allowing your organization to conduct data analytics and research without compromising the privacy of the data subjects.
Having said all of the above, in essence, you can think of pseudonymization as a protective veil over the personal data your organization collects and processes, which gives you a defense mechanism against data breaches and unauthorized access and subsequent peace of mind. Last but not least, pseudonymization upholds privacy standards such as those of the GDPR and fosters trust between your organization and your customers.
What does the GDPR say about Pseudonymization?
The General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, offers a series of principles related to the processing of personal data one of which is the principle of ‘integrity and confidentiality’ outlined in Article 5 (1)(f) where it is stated that personal data has to be “processed in a manner that ensures appropriate security of the personal data, including protection against unauthorized or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction or damage, using appropriate technical or organizational measures.”
Alongside this, Article 4(5) of the GDPR offers a definition for “pseudonymisation” as “the processing of personal data in such a manner that the personal data can no longer be attributed to a specific data subject without the use of additional information, provided that such additional information is kept separately and is subject to technical and organizational measures to ensure that the personal data are not attributed to an identified or identifiable natural person.”
In addition to this, Recital 26 of the GDPR says that “personal data which have undergone pseudonymisation, which could be attributed to a natural person by the use of additional information should be considered to be information on an identifiable natural person,” which means that pseudonymized personal data is still considered personal data by the GDPR.
Last but not least, Recital 28 of the GDPR encourages organizations to use pseudonymization because “the application of pseudonymisation to personal data can reduce the risks to the data subjects concerned and help controllers and processors to meet their data-protection obligations.”
The key takeaway here is that the GDPR doesn’t always define pseudonymization but it also seems to encourage it, sort of saying “You can still do your thing, but here’s a way to keep everyone safe while doing this, and also keep in mind that even with this method in place you still need to be careful.”
How is Pseudonymization Used Under GDPR?
The GDPR sets the gold standard for data protection practices worldwide, explicitly mentioning pseudonymization as a recommended measure to protect individuals' personal data. In addition to this, it also distinguishes between pseudonymization and anonymization, which falls outside the scope of the GDPR and is another way of processing the personal information of data subjects in such a way that it can no longer be associated with the data subjects through any means.
As mentioned earlier in this article, pseudonymization means the personal data is associated with a series of identifiers, consisting of numbers and/or letters, and can be decoded later on, which means it is still considered personal information.
Anonymization is when data is changed so much that there's no way to tell who it belongs to, not even by your organization. According to the GDPR, once the data is anonymized, it is no longer seen as personal data so the GDPR no longer covers it.
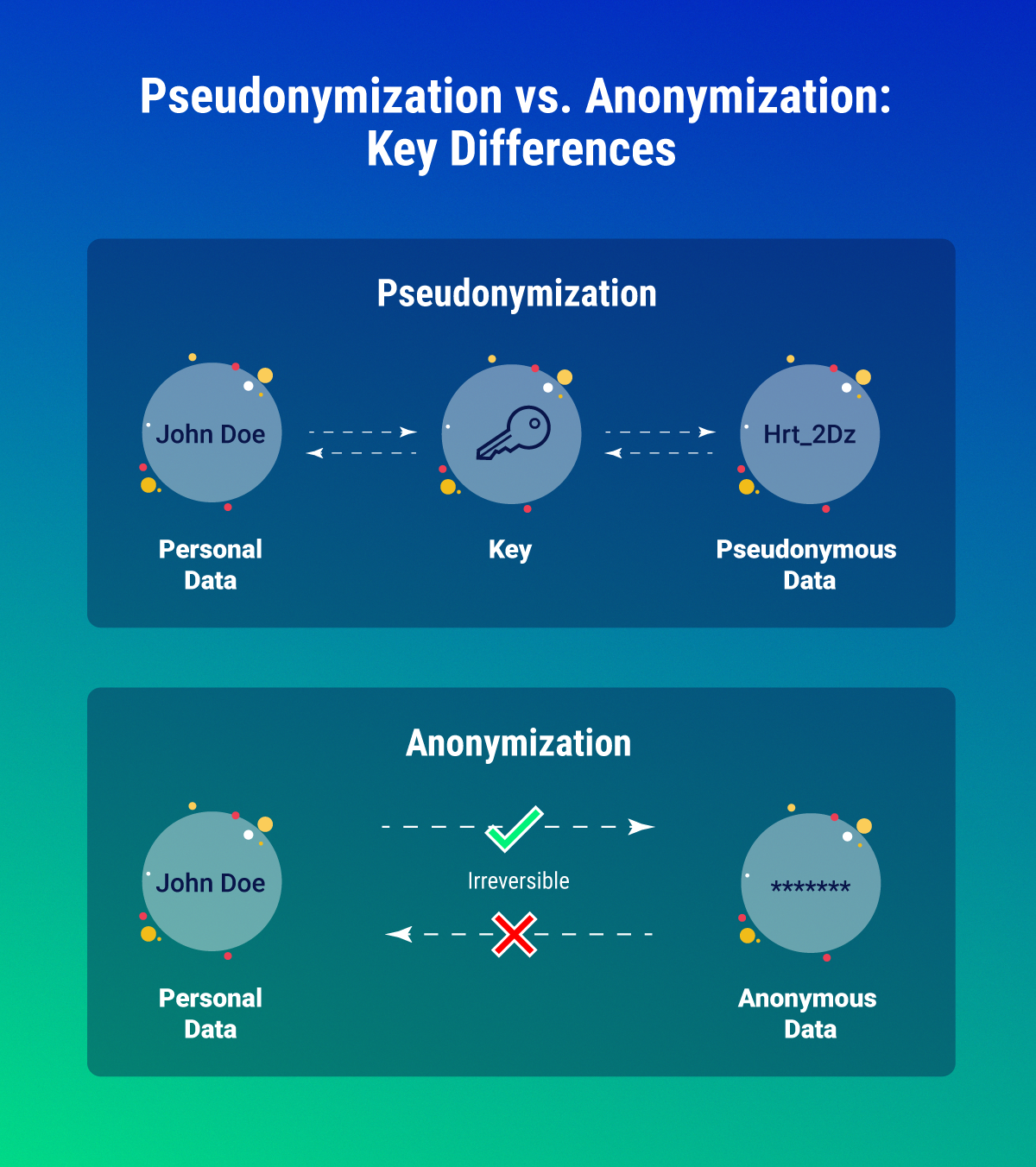
Here is a general example of pseudonymization versus anonymization:
What is the Difference Between Anonymization and Pseudonymization?
The fundamental difference between anonymization and pseudonymization lies in the reversibility of the process. Anonymization is irreversible, ensuring that data cannot be linked back to an individual, even by the data holder. On the other hand, pseudonymization is reversible with the aid of additional information, meaning that the data can still be associated with individuals under controlled conditions.
Imagine you have a secret nickname that only a few close friends know. If someone outside your friend group hears this nickname, they won't know it's you unless they have the key — the knowledge that the nickname refers to you. This is like pseudonymization. Your real name is hidden behind a nickname (or a code), but with the right key, someone can figure out who you are.
Now, imagine if instead of a secret nickname, you're given a totally random number that has nothing to do with you. Even if someone knew all the numbers and names in the world, they couldn't link that number back to you. This is like anonymization. Once your name is turned into that random number, there's no way to trace it back to you, even with a key.
So, the difference is:
- With pseudonymization, your identity is hidden, but someone with the right information can still figure out who you are.
- With anonymization, your identity is hidden so well that it's impossible to find out who you are, no matter what information someone has.
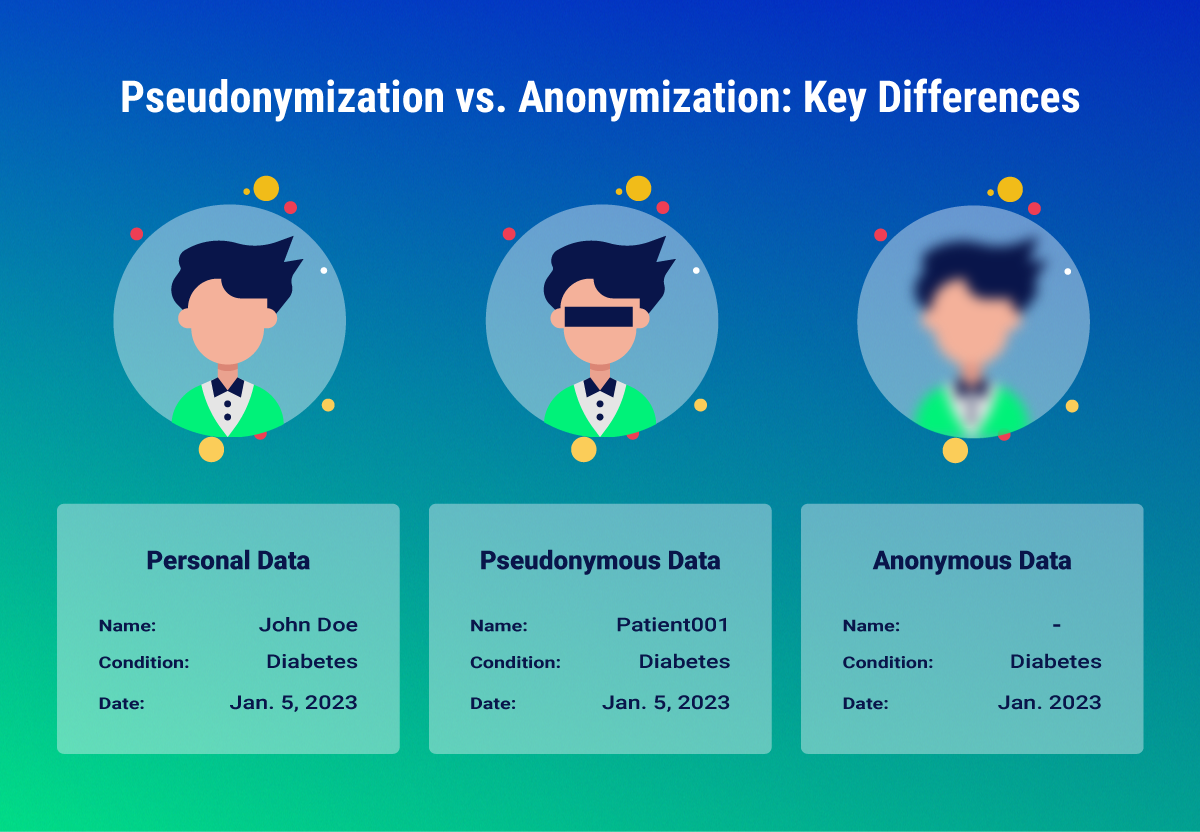
Here is an example of pseudonymization and anonymization applies to the same data set:
Let's consider a dataset from a healthcare provider that includes patient names, their conditions, and the dates they were diagnosed.
|
Original Dataset: |
Pseudonymized Dataset: |
Anonymized Dataset: |
|
1. John Doe - Diabetes - Diagnosed on January 5, 2023 |
1. Patient001 - Diabetes - Diagnosed on January 5, 2023 |
1. Condition: Diabetes - Diagnosed in January 2023 |
|
2. Jane Smith - Hypertension - Diagnosed on February 10, 2023 |
2. Patient002 - Hypertension - Diagnosed on February 10, 2023 |
2. Condition: Hypertension - Diagnosed in February 2023 |
|
3. Alice Johnson - Asthma - Diagnosed on March 15, 2023 |
3. Patient003 - Asthma - Diagnosed on March 15, 2023 |
3. Condition: Asthma - Diagnosed in March 2023 |
Applying Pseudonymization:
In pseudonymization, we replace names with a unique identifier, such as a patient ID, while keeping other data like conditions and diagnosis dates. This allows healthcare professionals to work with the data without directly exposing patient identities.
Here, "Patient001," "Patient002," and "Patient003" replace the real names. If necessary, a secure and separate key can match these IDs back to the actual patients. This setup is useful for internal reviews, research where patient tracking might be needed for follow-ups, or when aggregating data for treatment effectiveness studies without revealing personal identities.
Applying Anonymization:
For anonymization, we remove or aggregate any information that could potentially identify the patients. This might include altering diagnosis dates or removing specific conditions if they are rare enough to identify individuals.
In this anonymized version, specific identifiers are removed, and dates are generalized to just the month and year. This prevents any personal identification, ensuring the data can be used for broad statistical analysis, like studying the prevalence of conditions over time, without any risk of re-identifying the patients.
Anonymization provides a higher level of privacy protection and is suited for public sharing or high-level epidemiological studies where individual patient follow-up is not required. In contrast, pseudonymization balances the need for privacy with the utility of being able to link data back to individuals under controlled and secure conditions, useful in clinical studies or where patient consent allows for re-identification for further medical research or treatment.
What are the Benefits of Pseudonymization?
Pseudonymization is like giving someone a mask to wear. Even though they're part of a crowd, you can't tell who they are unless you have the special key to remove their mask. This simple idea helps keep personal information safe in many ways:
It Makes Personal Data Safer
Think of pseudonymization as putting a lock on data subjects’ data. Just like a bike lock keeps a bike safe from thieves, pseudonymization keeps personal information safe from hackers and people who shouldn't see it. By changing names or other details to something like a random number or code, it's much harder for hackers to figure out whose data they've got. This means even if they sneak into a place they shouldn't be, they can't do much with what they find.
It Helps Your Organization Follow the Rules
Keeping the personal data of individuals safe by your organization means you follow the rules of the GDPR. Its rules say that if you're collecting or using people's information, you need to protect it. Pseudonymization is a bit like cleaning your room because your parents asked you to. It's a good way to make sure you're doing what's expected to keep everything tidy and safe. By pseudonymizing data, your business shows that you’re serious about following these rules, which helps you avoid getting into trouble.
It Keeps Personal Data Useful
One great thing about pseudonymization, compared to making data completely anonymous, is that the data can still be used later on for important matters, such as, for example, researchers, who may need to study health information to learn more about certain diseases. With pseudonymization, they can look at the data they need without seeing personal details like names or exact birth dates. Later on, if they need to know more about a specific person's information for their study, they can use a special key to get the details they need, all while keeping that person's privacy safe.
Think of pseudonymization a bit like a superhero's mask. It hides the identity but allows the hero to keep doing important work. It protects people's information, it helps ensure your organization follows the GDPR’s rules, and still allows scientists and researchers, among others, to use the personal information for good purposes.
How can Clym help you with Data Privacy Compliance?
Clym offers you a comprehensive solution for managing your business’ compliance in alignment with global privacy laws. Featuring a user-friendly Cookie Consent Banner and a robust Consent Management Platform (CMP), Clym ensures your website meets global data privacy compliance standards while prioritizing user privacy.
Our platform simplifies compliance according to privacy regulations, allowing users to adjust their preferences seamlessly.
With Clym, your business can maintain data governance effortlessly, ensuring ongoing compliance and peace of mind for legal teams by minimizing the risk of non-compliance.
See us in action today by booking a demo or contacting us to discuss your specific needs.
Helpful Resources
If you’re not sure where to start but know for a fact that your business needs to make use of pseudonymization, here’s a helpful tip. The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) has published helpful resources consisting of both an explanation of the basic notion of pseudonymization and implementation solutions, such as the following:
FAQs about Pseudonymization
What is Pseudonymization?
Pseudonymization is the process of changing personal information like names or email addresses into a format (like a number or meaningless name) that can't easily be linked back to the individual without additional information. It's a key strategy to keep personal data safe and private, especially online, aligning with GDPR requirements.
How Does Pseudonymization Work?
Imagine your personal details being replaced with a unique code that only specific authorized persons can decode. Even if someone unauthorized accesses the data, they can't identify you without the key. This technique is crucial for maintaining privacy and security in data handling and processing.
What Does the GDPR Say About Pseudonymization?
The GDPR encourages the use of pseudonymization to protect personal data. It's considered a way to process data securely, ensuring protection against unauthorized access or loss, as outlined in Articles 4(5) and 5(1)(f) of the GDPR. Despite pseudonymizing data, the GDPR still treats it as personal information, emphasizing the importance of handling it with care.
How is Pseudonymization Used Under GDPR?
Pseudonymization is recommended by the GDPR to enhance data security. It's a reversible process, meaning data can be re-identified under controlled conditions, unlike anonymization which is irreversible. This allows for secure data analysis and processing while complying with GDPR standards.
What is the Difference Between Anonymization and Pseudonymization?
The main difference is reversibility. Anonymization is a permanent change where data can't be traced back to an individual, making it no longer personal data under GDPR. Pseudonymization, however, disguises the data but allows for re-identification with the right additional information.
What are the Benefits of Pseudonymization?
Pseudonymization secures personal data from unauthorized access, helps organizations comply with GDPR, and maintains the utility of data for analysis and research. It's like a protective veil over personal data, reducing the risk of breaches and misuse while enabling valuable data use under secure conditions.